Pasteur Eye Hospital
Eye Conditions
Contact Us
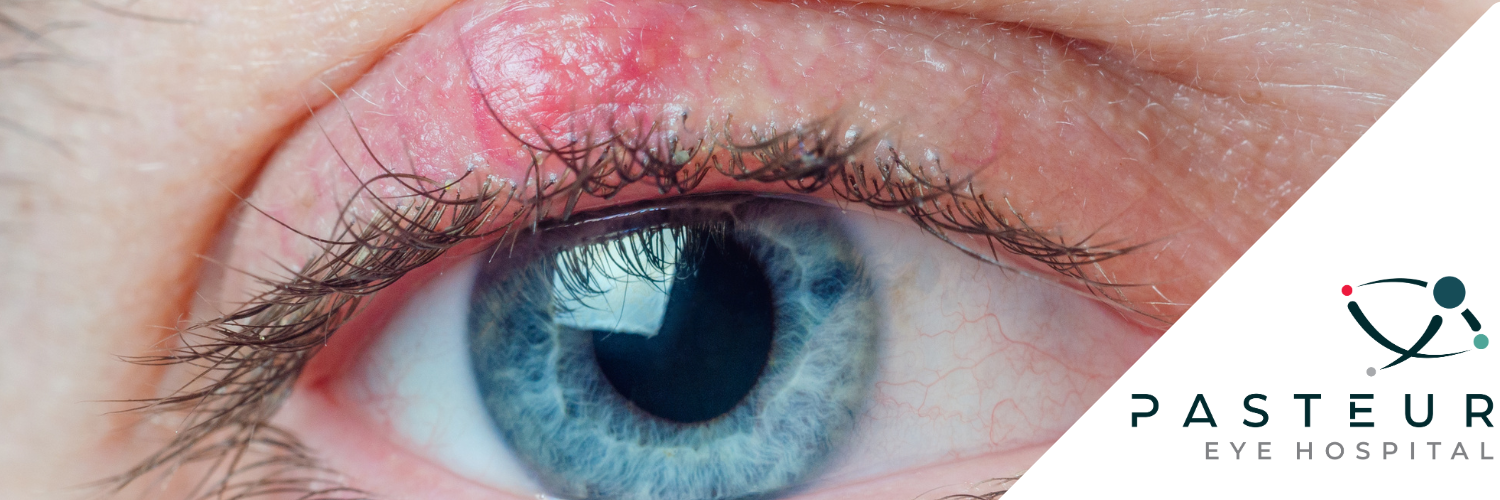
A chalazion is a common eyelid condition characterised by a slight swelling or lump resulting from a blocked gland. This type of eyelid lump, referred to as chalazia when more than one is present, frequently appears on the upper eyelid but can affect both eyes simultaneously. Chalazion often resolves and recurs, making it a persistent issue for some individuals.
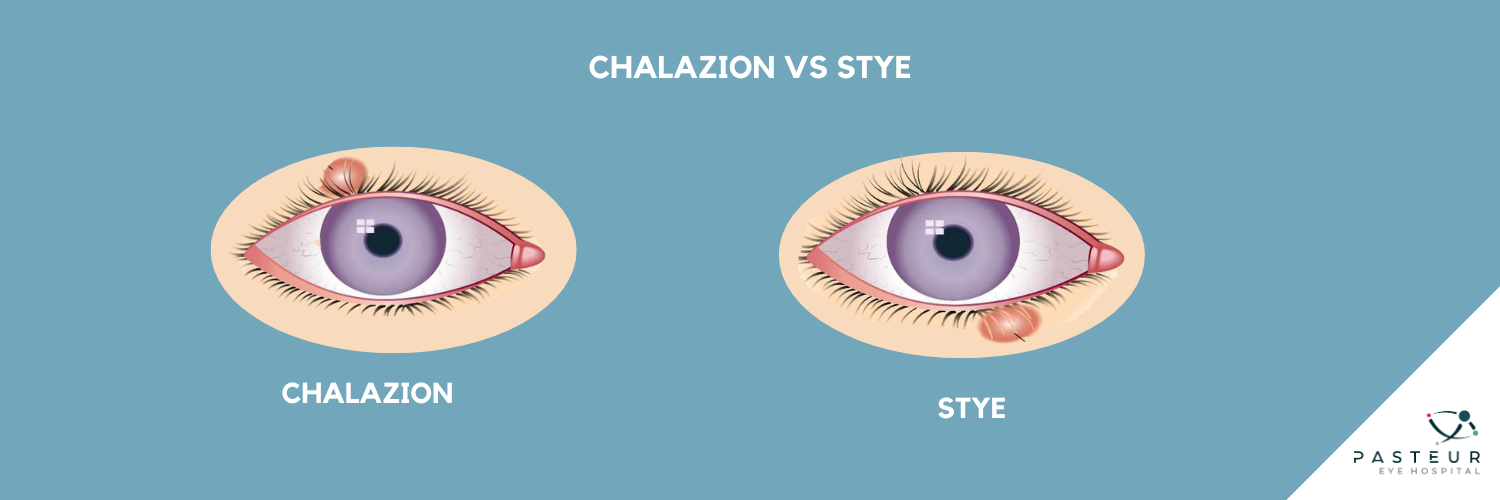
Differentiating between a chalazion and a stye can be challenging as both present as eyelid bumps.
A stye, typically painful and with a yellowish spot that may burst, forms along the edge of the eyelid or at the base of an eyelash due to an infection. In contrast, chalazion usually develops towards the middle of the eyelid and is generally less painful.
Occasionally, a stye can evolve into a chalazion if the infection clears, leaving some material trapped in the gland.
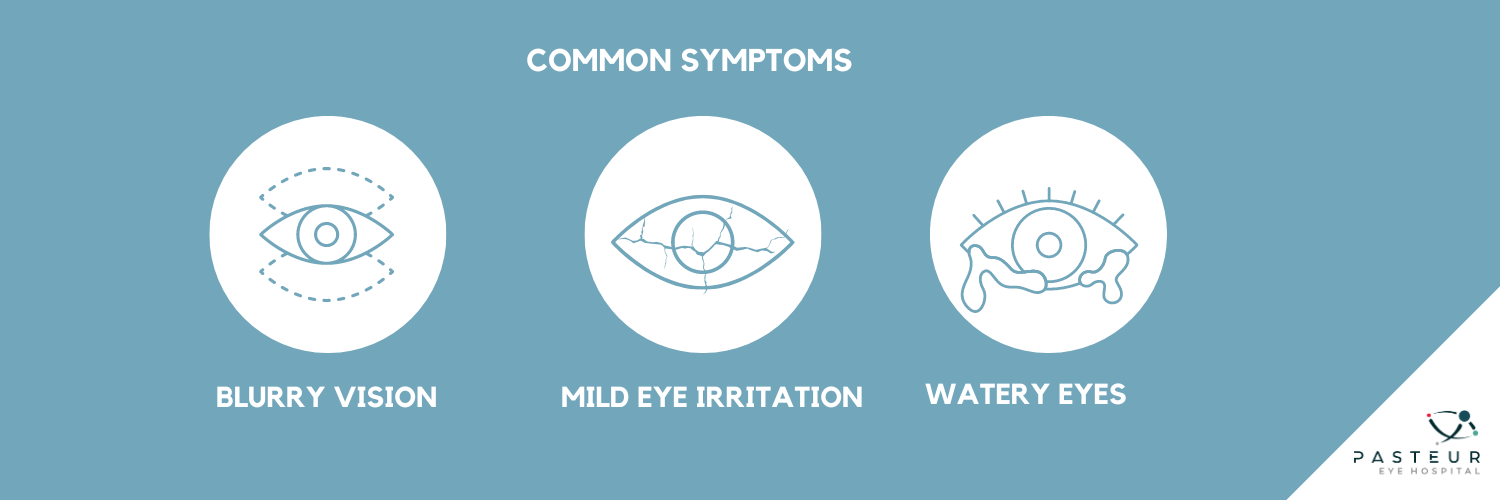
A chalazion starts as a red, swollen, and sore area on the eyelid. The pain often subsides within a few days, leaving a bump that can cause:
• Watery eyes
• Mild eye irritation
• Blurry vision
With proper home care, a chalazion typically resolves within a week. Even without treatment, it usually disappears in about 4-6 weeks. However, if a chalazion persists beyond a month, it is advisable to consult a doctor.
Chalazion occurs when the meibomian glands in the eyelids become blocked. These glands
produce oil that mixes with tears to keep the eyes moist and protected.
Factors that can lead to blockages include:
• Thickened oil production
• Inflammation
• Underlying health conditions such as rosacea, blepharitis, seborrheic dermatitis and viral infections
Chalazion is more common in adults than children and is associated with conditions like:
• Eyelid inflammation (blepharitis)
• Skin conditions (seborrheic dermatitis, acne rosacea)
• Health conditions such as diabetes
• The previous occurrence of chalazion
Diagnosing a chalazion typically involves a doctor reviewing symptoms and conducting an external eye and eyelid exam. Treating associated conditions like blepharitis can prevent recurrent chalazion.
Most chalazia can be resolved without treatment, but warm, moist heat applications using a clean washcloth can expedite healing. Maintaining eyelid hygiene with mild soap or eyelid scrubs can also help. Never squeeze or pop a chalazion, as this can worsen the condition.
Doctors may prescribe eye drops or creams in persistent cases. Severe cases might require a minor surgical procedure to drain the chalazion, typically performed in the doctor’s office under local anaesthesia.

Although it’s challenging to prevent chalazion entirely, you can reduce the risk by:
• Washing your hands frequently, especially before touching our eyes or handling contact lenses.
• Cleaning eyelids before bed to remove makeup and debris.
• Replacing eye makeup every 2-3 months and not sharing it
• Properly cleaning and disinfecting contact lenses
Consult a doctor if a chalazion doesn’t improve with home care within a month or if it recurs. Professional medical advice is crucial for persistent or troubling cases.
Chalazion is a common eyelid lump caused by blocked oil glands. While it often resolves independently, persistent or recurrent chalazion warrants medical attention. Maintaining good eyelid hygiene and seeking timely medical advice can effectively manage and prevent chalazion.
Understanding these aspects can help you recognise, treat, and prevent chalazion, ensuring better eyehealth and comfort.
Pasteur Eye Hospital
Eye Conditions
Contact Us
© Copyright 2022 Pasteur Eye Hospital. All Rights Reserved.
No article or picture may be reproduced\published without the written consent of Pasteur Eye Hospital.
Managed with ❤️ by Cuberoo